Case Project 7-3 Quarterly Review of Access Rights
All-time practices to bear a user access review
User entitlement reviews ensure only authorized users have access to essential systems and information. Uncover the steps of a user admission review and helpful best practices.
Controlling and regularly reviewing which employees have access to which systems and data isn't just enterprise...
security 101 -- information technology's a compliance necessity. Sarbanes-Oxley Human action, PCI DSS, HIPAA and GDPR all accept mandatory user access review requirements, which could land your company in hot water if non reviewed regularly.
Many enterprises use a diversity of identity and access management (IAM) mechanisms, such as role-based access control (RBAC) or the principle of to the lowest degree privilege (POLP) to secure privileged access in their systems. Merely, once these are in place, then what?
Remember about the number of employees that have quit or been terminated at your company in the past year. Then, add in the number of electric current employees who have changed roles or departments. If you work for a big arrangement, this number could be in the hundreds or even the thousands.
Now, consider the data, applications and systems those employees had or accept access to. Terminated employees may still hold the keys to some of the company's most valuable information. Electric current employees with user privilege account accumulation present merely as big a chance.
To counter these problems, it's critical to comport user access reviews.
What is a user access review and why is it important?
A user access review is the procedure of periodically assessing the rights of anyone who has admission to enterprise systems and data. Users tin can include employees, partners, third parties, service providers and vendors.
Performing user account reviews, besides known as account recertification, business relationship attestation or entitlement review, is critical to monitor, manage and audit the user account lifecycle from creation to termination -- and everywhere in between.
User access reviews should coincide with a well-divers user admission review policy. Reviews should be washed on a regular footing to prevent potential security problems.
Common user admission risks
The wrong access rights can result in malicious attacks or internal mistakes that could be detrimental to the company's make and its bottom line. Common access risks include the following:
- privilege creep
- inappropriate or unauthorized admission
- fraud
- access abuse
- internal threats, malicious and accidental
- account misconfiguration
- outdated user access policies
Users tin can become overprivileged for a number of reasons -- for instance, changing roles in a company and not having their access rights adapted to their new role, quitting or being fired yet retaining admission rights, mergers and acquisitions, and more.
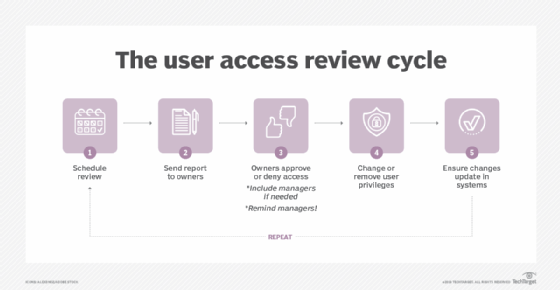
How to conduct a user admission review
Step ane. Define your access management policy
At minimum, a user access management policy should include the following:
An inventory of enterprise avails. List which assets users can exist granted access privileges to beyond your enterprise. Document all databases, applications, systems, networks, OSes, information centers, rooms, buildings, etc.
A list of owners for each nugget. Identify the possessor(s) of each asset. This could exist a manager, administrator or Information technology team, among others. Owners should and then provide a detailed list of the types of data and accessible content in their assets, which will map to access levels and roles.

Descriptions of user access levels and roles. Assign job roles and responsibilities and their access requirements down to a granular level. For example, some employees will need read-just access to data to perform their job functions, while some crave editing capabilities, and others will need permission to delete data. Providing the least privilege necessary for a job part is critical to eliminating user ID security gaps.
Reporting frequency and types. Dissimilar types of user access audits can exist put in place. Trigger-based account reviews are one-off updates initiated past predefined rules, such equally when an employee changes departments or is terminated. Other reviews are scheduled on a regular basis.
User admission reviews may be conducted per arrangement, per employee or equally a combination of the two. A per-system review will audit admission controls based on who has access to each system, while a per-employee review examines privileges based on the systems an employee accesses.
Deciding how often to bear reviews will vary by organization. Smaller companies may be able to review the entire policy more than frequently than large corporations, which may only appraise one organisation at a fourth dimension or examination a sampling and conduct a full review only when discrepancies occur. Depending on the system, reviews can exist run monthly, quarterly, biannually or annually. Inspect high-hazard assets more than often, while lower-gamble systems can be assessed less frequently.
When defining frequency, consider how to administrate your next review. Some businesses piece of work from previous reviews and follow the aforementioned processes, but this isn't advisable for all organizations, especially those that take changed a lot in a given time menstruation. For example, a visitor that has undergone a reorganization, adopted new applications or systems, or been involved in a merger or acquisition should revisit its review processes and schedules.
Deprovisioning processes. An enterprise user access review policy should also detail corporate provisioning and deprovisioning processes. Provisioning, the showtime step in the user account lifecycle, explains how access privileges are assigned to a new hire. Deprovisioning outlines how user IDs are revoked when an employee changes roles or is terminated. Removing access rights to enterprise assets is part of the deprovisioning and offboarding procedure, but it can be overlooked. Regular access reviews will notify managers and owners of bug in offboarding, enabling the company to update its processes and remediate whatsoever changes necessary.
Training and instructions on when to enlist others' help. An entitlement review is an enterprise-wide projection. While a CISO or security admin may own the chore, other C-level staff and managers should help ascertain and review admission controls. Remember, an effective squad requires constructive, hands digestible data. Many concern systems allocate user IDs and access controls in their own formats. Combining data from multiple systems can get complicated and confusing. Collate and simplify the data for owners. If data is difficult to read, owners may sign off on the report without conducting a thorough analysis.
Managers should also be enlightened of the access rights they're providing employees. Giving admission for the sake of giving access opens an enterprise to risk. Security awareness preparation can aid prevent managers from providing too many access privileges to employees, as well equally help them understand the risks associated with diverse roles and their level of access to enterprise assets.
Account attestation tin can be manual or programmatic. Manual user access reviews are often considered time-consuming and cumbersome. Programmatically, software helps with the task. For some organizations, directory services are sufficient, such as Active Directory for Windows or Lightweight Directory Access Protocol for Unix. These tools may non offer the granular-level business relationship recertifications needed by all businesses, nevertheless. IAM tools, such as Hitachi ID Identity Manager, IBM Security Identity Governance and RSA SecurID Access offer reporting options for user access reviews. Machine learning algorithms tin can also assistance streamline the process.
Step 2. Conduct the review
Once a clearly defined policy is in place, create a report of all databases, applications and systems, and determine who currently has access to them. Include all employees and third parties, such as vendors, service providers and consultants.
Ship a copy of the report to each asset possessor, who should so audit the list to verify who has access, at what level and whose admission privileges should be inverse or revoked. Sometimes, this is based on role, section or responsibility, while a more than granular approach is needed at other times. For example, responsibilities and privileges can vary for people in the aforementioned function.
In some reviews, owners may corroborate or refuse whole departments. Section managers then must verify or reject whether specific employees from their respective departments should be allowed admission. If an asset owner rejects a department'due south access privileges, the owner should notify the department director, who so should be given time to negotiate the case for access, if necessary.
Make certain owners sign off on the report by deadline.
Stride 3. Remediation and reporting
Once you lot receive all user account access reviews, execute changes based on the owners' reviews. Remove any revoked access, and update employees' privileges as needed. Generating a new user admission written report will verify changes have gone into result.
Finalize, impress and store the report. Finalized reports should include previous and current roles, access rights, who approved them, the names of the systems' owners and whatsoever notes or further deportment. This report provides an audit trail and bear witness of access recertification compliance.
At present is a good time to assess security gaps. For example, if a number of user IDs get revoked due to a specific policy from the provisioning process, it might be time to rethink corporate provisioning practices. The written report tin can besides measure out how well security policies and IAM strategies are working, also as whether admission policies during hiring, transferring or termination are efficient and still in line with the security model of your business.
Also, take time to assess your review procedure. What went well? Are at that place steps that could simplify the procedure next time? What ways could you make user access review more efficient?
Best practices for user access reviews
The admission review process is a critical component of any enterprise security program:
- Create an access control policy, and update every bit needed.
- Adopt a formal access review process.
- Perform regular audits.
- Encourage and crave involvement from employees and management.
- Use access command software features in IAM products, or consider deploying such products and features.
- Review access controls non merely when an employee is hired or terminated, but also when roles modify inside the organization.
- Define and certificate the segregation of duties, which involves splitting tasks and privileges for a specific process amid two or more than people.
Equally with everything in security, look the unexpected. Be sure to have a process in identify for unforeseen issues, such every bit if segregation of duty violations are detected or if a job office has been changed and needs to be updated in the principal list of admission levels and roles.
Some general IAM and access best practices include the following:
- Enforce POLP.
- Employ RBAC.
- Consider deploying two-factor or multifactor hallmark.
- Adopt a strong countersign policy.
- Adopt a naught-trust security strategy.
This was final published in July 2021
Dig Deeper on Identity and access management
-

How to stop malicious or accidental privileged insider attacks
-

What is identity and admission management? Guide to IAM
-

3 key identity management tips to streamline workflows
-
![]()
Security Think Tank: Get basic security policy right, and the rest will follow
Source: https://www.techtarget.com/searchsecurity/answer/How-to-conduct-a-periodic-user-access-review-for-account-privileges




